Cord tissue is the inner substance of the umbilical cord that attaches the developing embryo to the placenta during pregnancy and birth. Cord tissue is rich in mesenchymal stem cells and is derived from the umbilical cord, which supplies oxygen and nutrients to the baby until birth.
What makes cord tissue special?
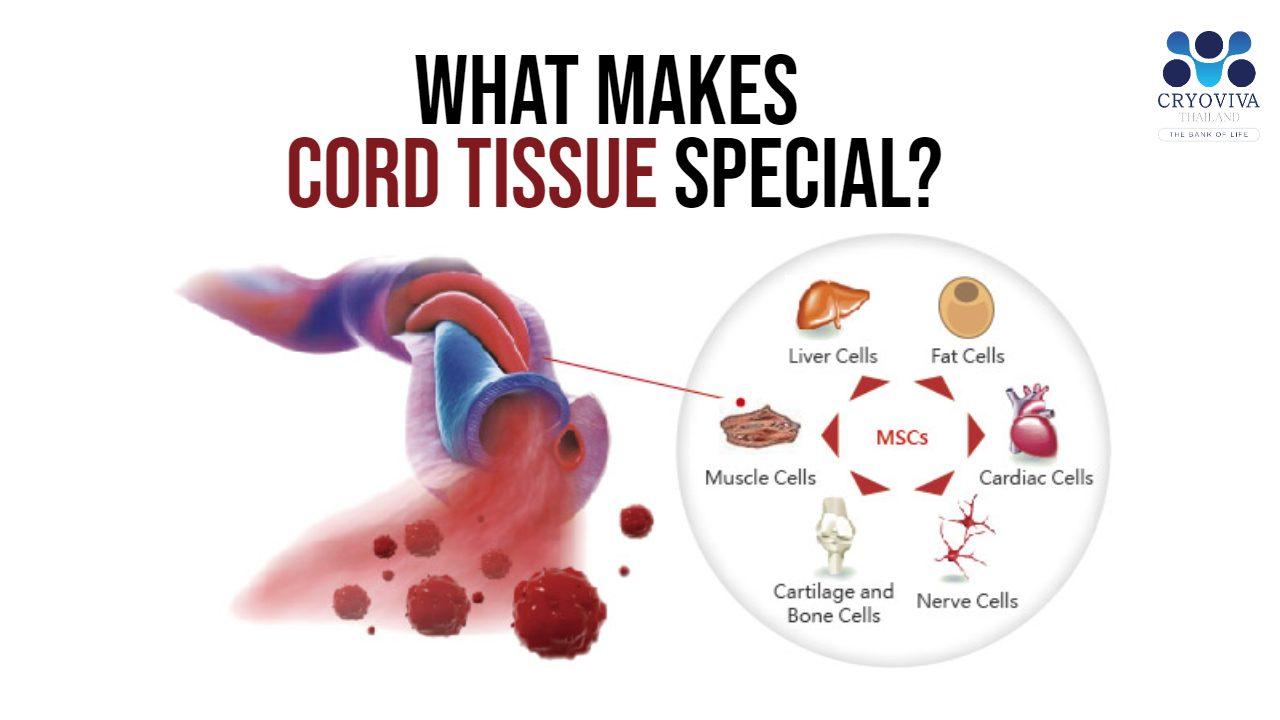
The therapeutic value of umbilical cord tissue is derived from its special characteristics. It is a rich source of mesenchymal stem cells, which may develop into numerous cell types, including bone, cartilage, and fat cells. These stem cells can differentiate into cells, which help repair diseased or injured tissues.
The profusion of mesenchymal stem cells is one distinguishing characteristic of umbilical cord tissue. These stem cells are younger, more flexible, and have a higher proliferative capacity than those derived from other sources, such as bone marrow or adipose tissue. Moreover, cord tissue contains progenitor cells that generate blood and immune cells.
The stem cells can be isolated and grown easily in large quantities under controlled laboratory conditions. They are safe because the donor is not harmed. Compared to other sources, umbilical cord tissue stem cells have a lower risk of rejection after transplantation.
Additionally, they are devoid of ethical concerns, unlike embryonic stem cells. Due to these unique qualities, umbilical cord tissue banking for future therapeutic applications is gaining prominence.
Read more: https://shorturl.at/nuCE9